Photo credit:halodx.com
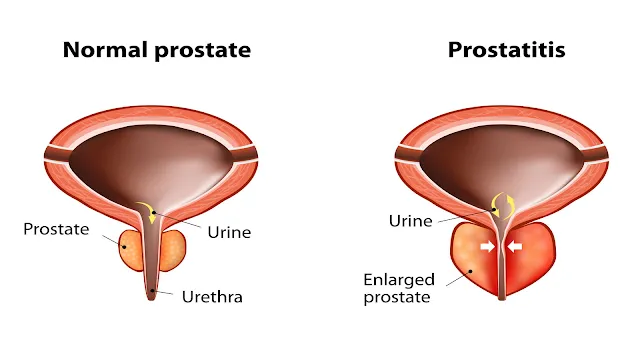
The primary cause of prostate enlargement, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is not fully understood. However, it is thought to be related to hormonal changes that occur as men reach 12.
(TOC)
Here are several important factors:
Here are
several important factors:
Hormonal Changes: As men age, the
balance of hormones in their bodies alters. This includes an increase in
dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that can promote prostate development.1.
Age: The chance of having BPH rises with age. It is relatively frequent among
men over the age of 60
Family History: Genetics may have a
role. Men with a family history of prostate problems are more prone to developing
BPH2.
Other Health Conditions: Diabetes
and heart disease can also lead to the development of BPH2.
If you have any specific concerns or symptoms, you
should always seek the advice of a healthcare expert. They can offer
individualized advice and treatment alternatives.
Its role in male reproductive health.
The prostate's principal purpose is to create a fluid
that accounts for a considerable amount of semen. This fluid protects and
energizes sperm, allowing them to successfully fertilize an egg during
reproduction.
What are the symptoms of prostate enlargement?
Prostate enlargement, also known as benign
prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), can produce a range of urinary symptoms. Here are
a few common ones.
1. Frequent urinating, particularly
at night (nocturia).
2. Urgency: A sudden and intense
need to urinate.
3. Difficulty commencing urination:
Struggling to urinate or straining while doing so.
4. Weak urine stream refers to an
intermittent or weak flow of urine.
5. Dribbling occurs at the end of
urine.
6. Incomplete bladder emptying: A
sensation that the bladder is not fully empty after urination.
7. Urinary retention refers to the
inability to pee, which can cause medical emergencies.
8. Blood in urine: Urine may
occasionally include blood.
If you have any of these symptoms, you should speak with a healthcare expert.
How is BPH treated?
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) can be treated using
a variety of approaches, depending on the severity of the symptoms and the
patient's overall health. Here are a few popular therapy options:
Lifestyle
Changes: Lifestyle changes such as minimizing fluid intake
before bedtime, restricting caffeine and alcohol consumption, and practicing
bladder training can all help control minor symptoms.
Medications:
Alpha
Blockers: These drugs, such as tamsulosin and alfuzosin, relax
the muscles of the prostate and bladder neck, increasing urine flow.
5-Alpha
Reductase Inhibitors: These medications, such as finasteride and
dutasteride, reduce the prostate by inhibiting the hormonal changes that drive
prostate growth.
Combination
Therapy: To achieve better results, alpha-blockers and 5-alpha
reductase inhibitors are sometimes used together.
Minimally
intrusive Procedures: These are less intrusive than surgery and
can effectively treat moderate to severe symptoms.
Transurethral
Microwave Thermotherapy (TUMT): This treatment uses microwave
energy to eliminate excess prostate tissue.
Transurethral
Needle Ablation (TUNA): This procedure uses radiofrequency
energy to heat and kill prostate tissue.
Surgical
Options: When alternative therapies fail to relieve severe
symptoms, surgery may be required.
Transurethral
Resection of the Prostate (TURP) is the most common surgical treatment that
involves removing a portion of the prostate.
Laser surgery is a
procedure that uses laser energy to remove or shrink extra prostate tissue.
Prostatectomy is the
removal of the prostate gland, which is often reserved for extremely big
prostates or when other treatments have failed.
Newer Treatments:
Emerging treatments for BPH include prostatic urethral lift (UroLift) and water
vapor therapy (Rezum), which have shown promising outcomes.
It is critical to
consult with a healthcare expert to decide the best treatment based on
individual symptoms and health problems.
What are the potential side effects of BPH medications?
Medications for
benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) might help manage symptoms, but they may
potentially have negative effects. Here are some common ones for the primary
categories of BPH medications:
Alpha-blockers
These drugs relax the muscles of the prostate and bladder neck, which improves
urine flow. Common side effects include:
• Dizziness.
• Headaches.
• Fatigue.
• Low blood pressure.
• Retrograde ejaculation occurs when semen flows backward into the bladder
rather than out via the penis.
5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors.
These medications reduce the prostate by inhibiting the hormonal changes that
drive prostate development.
Common side effects include
• Reduced sexual urge.
• Erectile dysfunction.
• Disorders related to ejaculation.
• Breast discomfort
or enlargement.
Phosphodiesterase-5
inhibitors.
These are sometimes prescribed to treat both BPH and erectile dysfunction. Common side effects include
• Headaches.• Flushing.
• Indigestion
• Nasal congestion.
Combination Therapy
Combining alpha-blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors can be more effective, but it also increases the risk of having negative effects from both types of medications1.
Any side effects you experience should be discussed with your healthcare practitioner so that they can help you manage them or alter your treatment plan as needed.
What lifestyle changes can help supplement BPH medications?
Lifestyle adjustments can considerably supplement drugs for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Here are some successful strategies123:Fluid Management:
Limit fluid intake in the evening, particularly before bedtime, to reduce midnight urination.
Avoid diuretics: Reduce coffee and
alcohol, as they can increase urine production.
Dietary adjustments:
A healthy diet should include a variety of fruits, vegetables, and entire
grains.
Reduce your consumption of red meat and high-fat foods, as they can increase
symptoms.
Physical Activity:
Regular physical activity can help improve general health and lessen BPH
symptoms.
Bladder Training:
Scheduled voiding: To train your bladder, urinate at regular intervals.
Double voiding: After urinating, wait a few moments before attempting to
urinate again to ensure that the bladder is empty.
Pelvic floor exercises:
Kegel exercises: Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles can aid with urine
control.
Avoid Certain Medications.
Decongestants and antihistamines can cause urine retention, so avoid them if
feasible.
Stress Management:
Relaxation techniques, such as yoga and meditation,
can reduce stress and relieve urinary symptoms.
Adding these lifestyle adjustments to your prescribed meds can help you control
BPH symptoms more effectively. Always talk with your doctor before making major
changes to your lifestyle.
Are there any particular foods that can exacerbate BPH symptoms?
Yes,
certain foods may increase the symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Here are some meals and beverages to be cautious about:
Red Meat: A high intake of red meat,
such as beef and pork, can worsen BPH symptoms.
Dairy items: Full-fat dairy items
such as milk, cheese, and butter may cause prostate problems.
Processed foods are heavy in preservatives and additives, which can harm prostate health.
Making dietary changes to reduce
or avoid these foods can help manage BPH symptoms more successfully.
A diet high in fruits,
vegetables, and healthy fats, such as the Mediterranean diet, can help with
prostate health.
What are some prostate-friendly foods to add to my diet?
Including prostate-friendly foods in your diet can assist promote prostate health and potentially lower your risk of prostate problems.
Some very beneficial foods.
Tomatoes include lycopene, an antioxidant that may lower the risk of prostate
cancer. Cooked or processed tomatoes, such as tomato sauce and paste, are
particularly rich sources.
Cruciferous
Vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, and kale have
chemicals that may help prevent cancer.
Fatty
fish,
such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which
have anti-inflammatory qualities.
Berries:
Strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries are abundant in antioxidants, which
can help cells resist damage.
Nuts,
particularly Brazil nuts, are high in selenium, and walnuts contain omega-3
fatty acids.
Green
tea
contains antioxidants called catechins, which may help prevent prostate cancer.
Soy
Products: Foods such as tofu and soy milk contain isoflavones,
which may protect the prostate.
Citrus
fruits, such as oranges, lemons, and grapefruits, have
significant levels of vitamin C, which can benefit overall health.
Pumpkin seeds are high in zinc, which is beneficial for
prostate health.
Incorporating these foods into a well-balanced diet can help keep your prostate
healthy. If you have any dietary limitations or health issues, it's always a
good idea to speak with a doctor or a nutritionist.
Tell me about how exercise helps to preserve prostate health.?
Exercise is essential for prostate health and can help manage or reduce
the risk of prostate-related conditions such as benign prostatic hyperplasia
(BPH) and prostate cancer.
Here are some key benefits of regular physical activity for prostate health.
Regular exercise, even at moderate levels such as walking, can help lessen BPH symptoms. Physical activity boosts blood circulation and lowers inflammation, which can help with urinary problems caused by an enlarged prostate1.Regular exercise has been related to a lower chance of acquiring prostate cancer. Exercise helps people maintain a healthy weight, which is crucial because obesity is a risk factor for prostate cancer2.
Exercise benefits cardiovascular health
strengthens the immune system,
and promotes healthy weight management. Exercise can promote recovery for men
after prostate cancer therapy by managing side effects and promoting general
well-being2. It can reduce tiredness, increase muscle strength, and improve
quality of life both during and after treatment3.
Supports Pelvic Floor Health: Kegel exercises, strengthen the pelvic floor
muscles, help improve urine control and alleviate BPH2 symptoms.
Recommended Types of Exercise
Aerobic Exercise: Walking,
jogging, swimming, and cycling are all beneficial to general health and can
help alleviate prostate-related discomfort.
Strength training, such as lifting weights or utilizing resistance bands, can
assist increase muscle mass and enhance metabolic health.
Pelvic Floor Exercises: Kegel exercises target the pelvic floor muscles and
help improve urine control.
Incorporating a variety of these workouts into your daily routine can bring
numerous prostate health benefits. Always contact a healthcare provider before
beginning any new exercise regimen, especially if you have pre-existing health
concerns.
When to See a Doctor?
If you are suffering signs of prostate enlargement such as difficulty urinating, frequent urination, or urine retention, you should seek medical attention. Early detection can help control the disease and avoid problems.Conclusion
Prostate enlargement is a typical problem as men age, owing to hormonal changes
and genetic factors. Understanding the reasons, recognizing symptoms, and
seeking appropriate therapy can help men maintain their prostate health and
improve their quality of life.
FAQs about prostate enlargement.
What age does prostate enlargement
normally start?
Prostate enlargement frequently begins after the age of 40, and the risk
increases as men age, with the majority of instances happening beyond the age
of 60.
Can prostate enlargement be reversed
naturally?
While prostate enlargement cannot be reversed naturally, lifestyle
adjustments such as a good diet and regular exercise can help alleviate
symptoms.
How can nutrition affect prostate
health?
A diet high in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats can benefit prostate
health, whereas high-fat, processed meals may raise the chance of enlargement.
Is prostate enlargement equivalent to
prostate cancer?
No, prostate enlargement (BPH) is not a malignant condition. However, it
can cause symptoms similar to prostate cancer, therefore regular screenings are
recommended.